Understanding the Basics of Semantic Search
Semantic search is transforming how we interact with search engines. It goes beyond simple keyword matching. Instead, it focuses on understanding the intent behind a query. This approach aims to deliver more relevant results. Semantic search engines use advanced technologies. These include artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP). They interpret the context and meaning of search terms. This allows them to provide more accurate answers.
The shift from keyword search to semantic search is significant. It reflects a move towards more intuitive search experiences. Understanding the basics of semantic search is crucial. It helps in optimizing content for modern search engines. This knowledge is valuable for digital marketers and SEO professionals. It can enhance their strategies and improve search visibility. In this guide, we will explore the fundamentals of semantic search. We will also discuss its impact on search engine optimization.
Table of Contents
 What is Semantic Search? Defining the Concept
What is Semantic Search? Defining the Concept
Semantic search is a method that enhances search accuracy. It does this by understanding the searcher’s intent and the contextual meaning of terms. This goes beyond just matching exact keywords in a query.
In semantic search, engines focus on user intent. This involves considering synonyms, context, and user behavior. It allows them to deliver more personalized and relevant results.
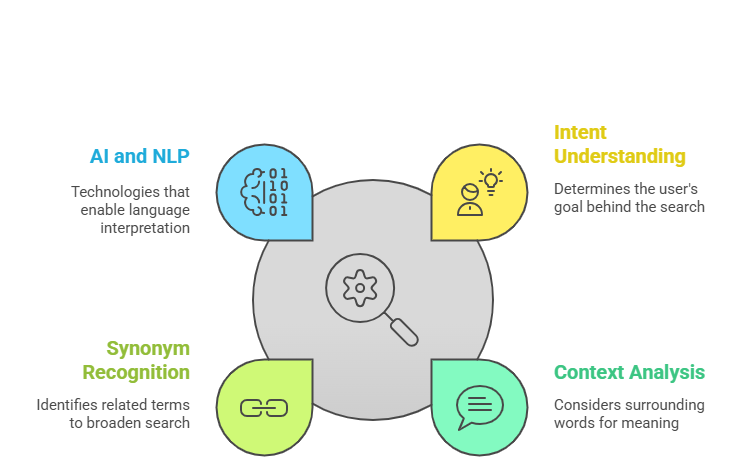
Key Features of Semantic Search:
- Intent Understanding: Determines what the user is looking to achieve.
- Context Analysis: Considers surrounding words and phrases to gather meaning.
- Synonym Recognition: Identifies related terms to broaden understanding.
Semantic search engines leverage technologies like AI and NLP. These tools enable them to interpret human language accurately. As a result, search outcomes become more aligned with what the user actually wants.
Overall, defining semantic search highlights how it transforms the user experience. It moves the focus from simple keyword matching to a deeper understanding of language.
How Does Semantic Search Work?
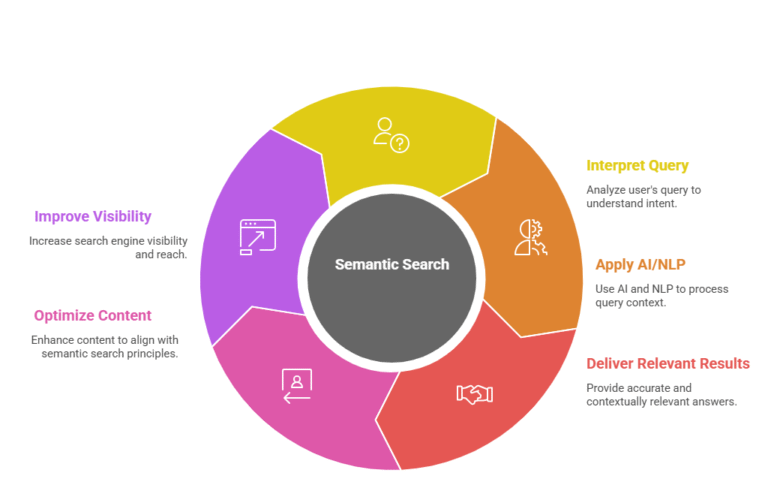
Semantic search works by employing sophisticated algorithms. These algorithms aim to grasp the intent and context behind user queries. It differs from traditional approaches that focus on exact keyword matches.
The process starts with query analysis. Here, the search engine dissects the user’s input. It evaluates potential intents and identifies the main subject matter.
After understanding the query, the engine delves into contextual cues. This includes examining synonyms, related phrases, and prior search behaviors. Such insights help refine the search to better match user intent.
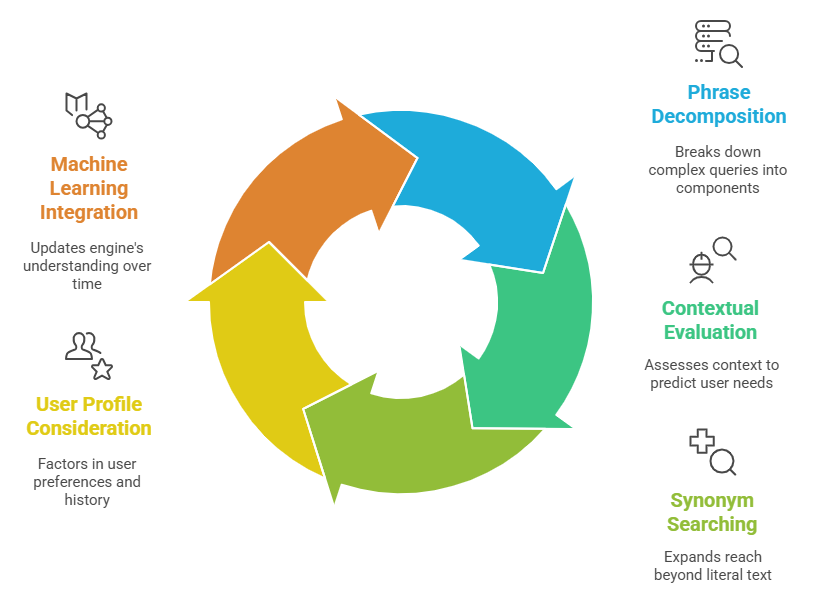
How Semantic Search Processes Queries:
- Phrase Decomposition: Breaks down complex queries into understandable components.
- Contextual Evaluation: Assesses context to predict the user’s needs.
- Synonym Searching: Expands reach beyond the literal text input.
AI and NLP are central to semantic search. These technologies power the ability to interpret nuanced language. For instance, Natural Language Processing enables machines to comprehend grammar and sentence structure.
Semantic search engines also consider user profiles. They factor in location, past searches, and user preferences. This allows them to tailor results to individual users, further enhancing relevancy.
The advancement of machine learning complements these efforts. It continuously updates the engine’s understanding. Over time, this leads to even more precise search results.
By integrating these components, semantic search delivers enriched experiences. It shifts from a rigid keyword-based model to an intuitive understanding of user intent. This approach significantly improves the quality of search outcomes.
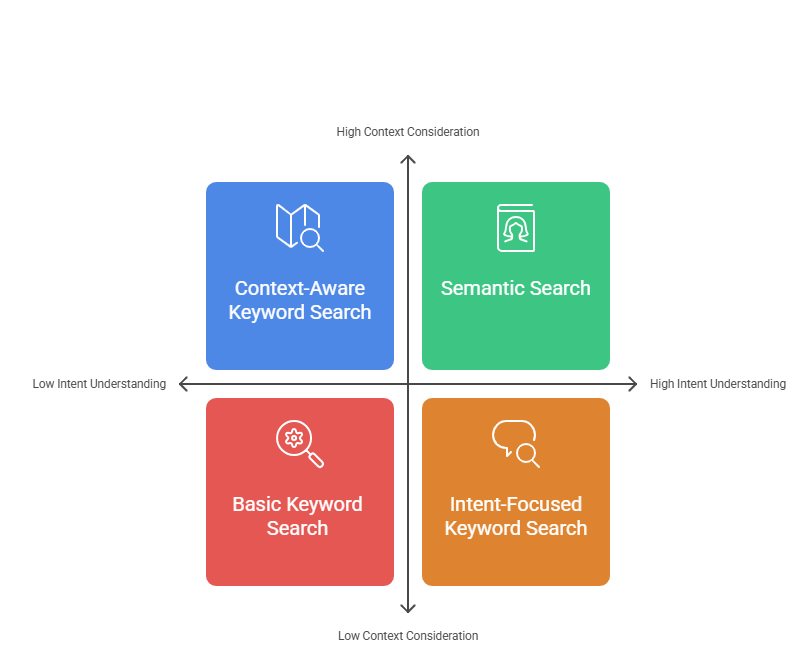
Semantic Search vs Keyword Search: Key Differences
Semantic search and keyword search serve different purposes. Keyword search focuses on finding exact word matches. Semantic search delves deeper, analyzing meaning and context.
One major advantage of semantic search is its ability to understand user intent. Keyword search limits results to the specific terms used. This means it can miss out on relevant information that uses different wording.
In contrast, semantic search interprets queries. It looks for synonyms and related concepts. This allows it to produce more relevant and comprehensive results.
Key Differences Between Semantic and Keyword Search:
- Intent Understanding: Semantic search focuses on user intent rather than word matches.
- Context Consideration: It evaluates the surrounding context of search terms.
- Word Relationships: Semantic search uses synonym detection to widen the search scope.
Semantic search adapts to natural language queries better. This adaptability suits the rise in voice search and conversational AI. Meanwhile, traditional keyword search struggles with such complexities.
Ultimately, semantic search offers a user-focused approach. It aims to deliver results based on meaning, not just matching strings. This shift is essential for modern search engines as they evolve to meet user expectations.
The Role of AI and NLP in Semantic Search
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in semantic search. It helps search engines understand complex queries. Without AI, interpreting the nuances of human language would be nearly impossible.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is another key technology. NLP enables machines to comprehend and analyze human speech. This processing is vital for correctly interpreting user queries in context.
AI and NLP work together in semantic search engines. Their integration allows the engines to grasp the intent behind search terms. This results in more accurate and relevant query resolutions.
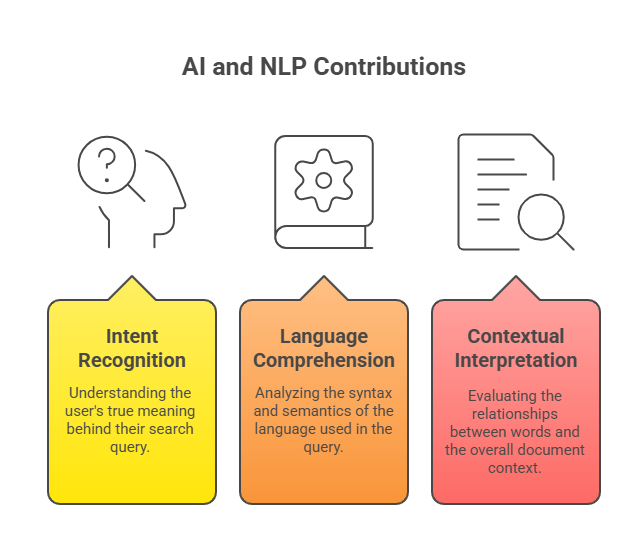
Contributions of AI and NLP in Semantic Search:
- Intent Recognition: Understanding what the user truly means.
- Language Comprehension: Analyzing syntax and semantics of language.
- Contextual Interpretation: Evaluating word relationships and document context.
Ultimately, the fusion of AI and NLP enriches semantic search. It allows for continuous learning and improvement. As AI evolves, so does the ability of search engines to deliver even better results. This synergy enhances the overall search experience for users, making it more intuitive and satisfying.
Core Components of a Semantic Search Engine
Semantic search engines rely on several key components to function effectively. These components work in tandem to comprehend and process search queries. Understanding each can shed light on how results are accurately generated.
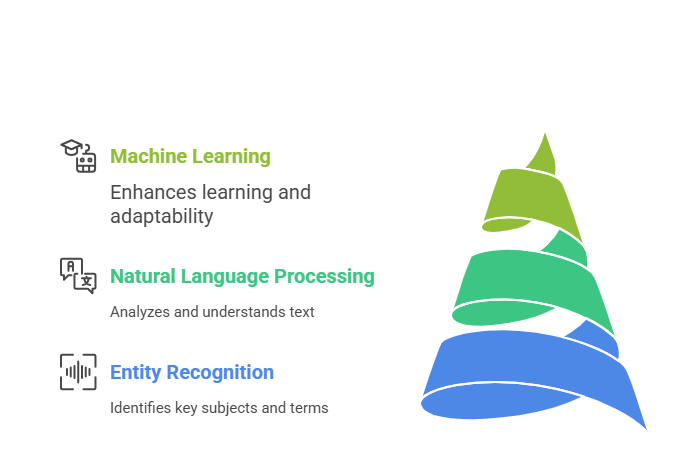
First, we have entity recognition. This identifies key subjects or entities within a query. It’s essential for matching queries with relevant data sources.
Next, natural language processing (NLP) plays a vital role. NLP analyzes the structure and meaning of text. This allows the search engine to understand the syntax and semantics of user queries.
Then there is machine learning. It powers the engine’s capacity to improve over time. By learning from previous queries, the engine refines its understanding and results.
Key Components of Semantic Search Engines:
- Entity Recognition: Identifies key subjects and terms.
- Natural Language Processing: Analyzes and understands text.
- Machine Learning: Enhances learning and adaptability over time.
Finally, these components together enhance the search process, ensuring it’s not just about matching keywords, but truly understanding user intent. This holistic approach to search changes the user experience profoundly, delivering more precise and relevant results.
Semantic Search Tools and Technologies
With the rise of semantic search, various tools and technologies have emerged to support its implementation. These tools are crucial for businesses aiming to optimize content and enhance search experiences.
Knowledge Graphs are foundational technologies in semantic search. They map relationships between different concepts, enabling a deeper understanding of queries. These graphs help search engines identify context and relevance more effectively.
Another essential technology is machine learning algorithms. These algorithms analyze patterns within search data, allowing the search engine to predict and adapt to user needs over time. They help in continuously refining search accuracy.
Natural language processing (NLP) tools are also vital. These tools interpret and translate human language into data readable by machines. This interpretation is pivotal for crafting search results that reflect user intent.
Key Semantic Search Tools:
- Knowledge Graphs
- Machine Learning Algorithms
- NLP Tools
By leveraging these technologies, semantic search systems can surpass traditional methods, offering users a more intuitive and effective search experience. They transform how information is accessed, meeting users’ needs in a more precise and context-aware manner.
Semantic Search Examples in Action
Semantic search examples highlight how advanced search engines function today. These examples illustrate practical applications, demonstrating their importance and effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
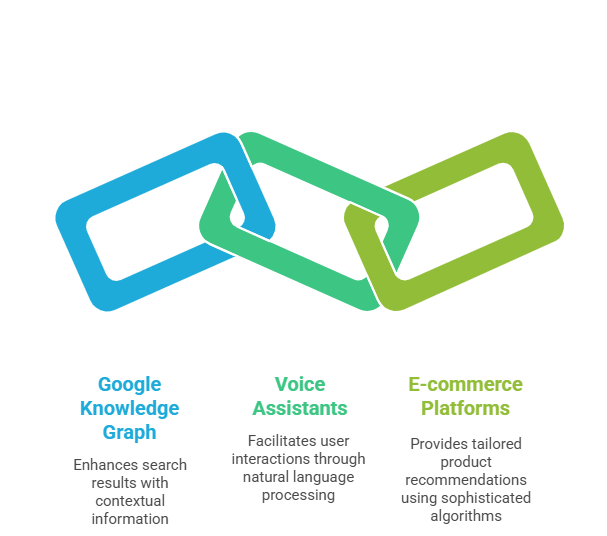
Google’s Knowledge Graph is a prime illustration of semantic search. It provides rich, contextually relevant data alongside traditional search results. By understanding the relationships between entities, it delivers more intuitive answers.
Voice assistants, such as Siri and Alexa, rely heavily on semantic search. They interpret voice queries, understanding user intent and providing accurate responses, even for ambiguous or conversational inquiries.
E-commerce platforms also benefit from semantic search. By employing semantic search engines, these platforms can suggest products based on user preferences, improving customer satisfaction and retention.
Real-World Applications:
- Google Knowledge Graph
- Voice Assistants (Siri, Alexa)
- E-commerce Product Recommendations
These examples showcase the ability of semantic search to transform how users interact with information. The focus shifts from simple keyword matching to understanding and satisfying user intent. As semantic technologies evolve, their influence on search experiences will continue to grow, providing ever-increasing value and efficiency to users worldwide.
Benefits of Semantic Search for Users and Businesses
Semantic search offers numerous advantages for both users and businesses. It has revolutionized search experiences, prioritizing relevance and accuracy.
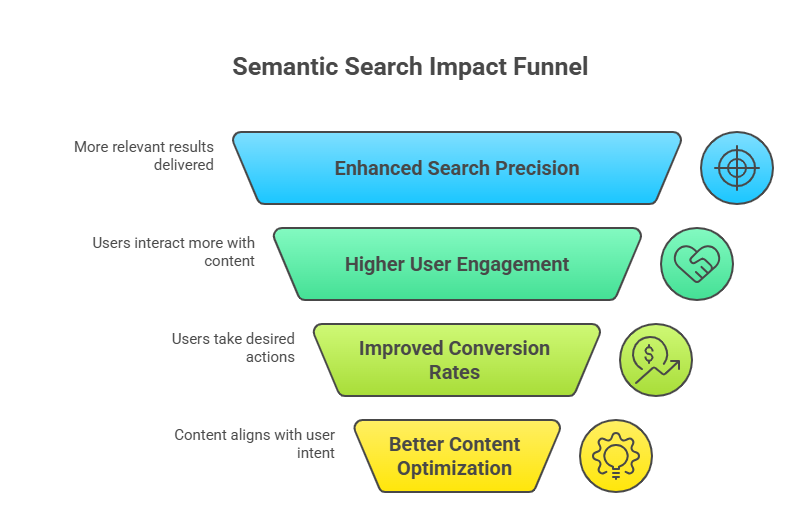
For users, semantic search enhances search precision. It considers the context and intent behind queries, providing results tailored to specific needs. This leads to a more engaging and satisfactory search experience.
Businesses benefit from improved user engagement and conversion rates. By aligning content with user intent, they can attract the right audience more effectively. This alignment reduces bounce rates and increases the potential for conversions.
Semantic search also supports better content strategy. Companies can optimize content based on sophisticated algorithms, ensuring higher visibility and relevance in search results.
Advantages of Semantic Search:
- Enhanced search precision
- Higher user engagement
- Improved conversion rates
- Better content optimization
Overall, semantic search not only improves the end-user experience but also offers significant business advantages. As search engines evolve, businesses that adapt to semantic strategies will likely outperform those relying solely on traditional methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Semantic Search
While semantic search has many benefits, it also faces challenges. Understanding natural language is complex, and even advanced systems struggle with nuances and ambiguities.
Search engines may misinterpret user intent, particularly in complex queries. This can lead to irrelevant results, frustrating users despite overall improvements.
Another limitation is the significant computational power required. Semantic search processes vast amounts of data to provide accurate results, which demands robust systems and technologies.
Key Challenges:
- Understanding nuances in language
- Misinterpreting complex queries
- High computational requirements
Additionally, there are privacy concerns related to user data collection. Personalizing search results involves analyzing user behavior, which may be intrusive. Balancing personalization with privacy is crucial as semantic search continues to evolve.
The Future of Semantic Search: Trends and Predictions
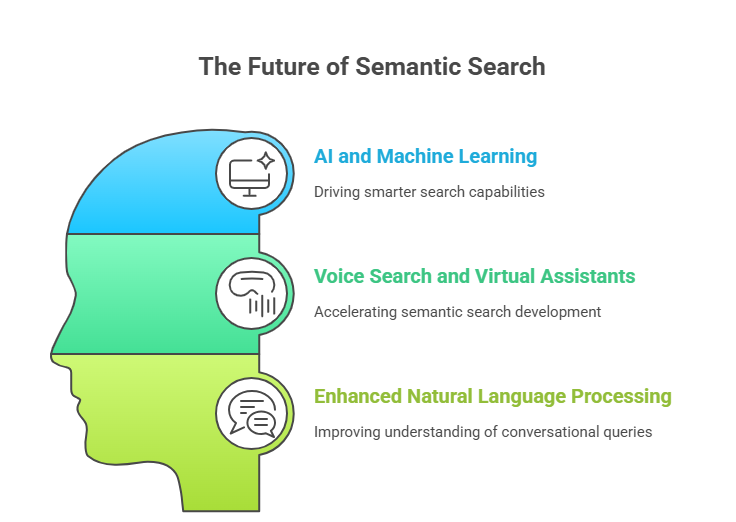
Semantic search is poised to transform further, driven by ongoing technological advances. AI and machine learning are key to this evolution, offering smarter search capabilities. These advancements will undoubtedly improve search accuracy and efficiency.
Voice search and virtual assistants are accelerating semantic search development. As more users adopt voice-enabled devices, search engines must better understand conversational queries. This will necessitate enhanced natural language processing.
Future Trends:
- Increased reliance on AI and machine learning
- Growth in voice search and virtual assistants
- Enhanced natural language processing capabilities
The ability to deliver highly personalized search experiences is a major focus. By leveraging user data and preferences, search engines aim to provide tailored results. This trend signifies a shift toward a more intuitive, user-centered search future.
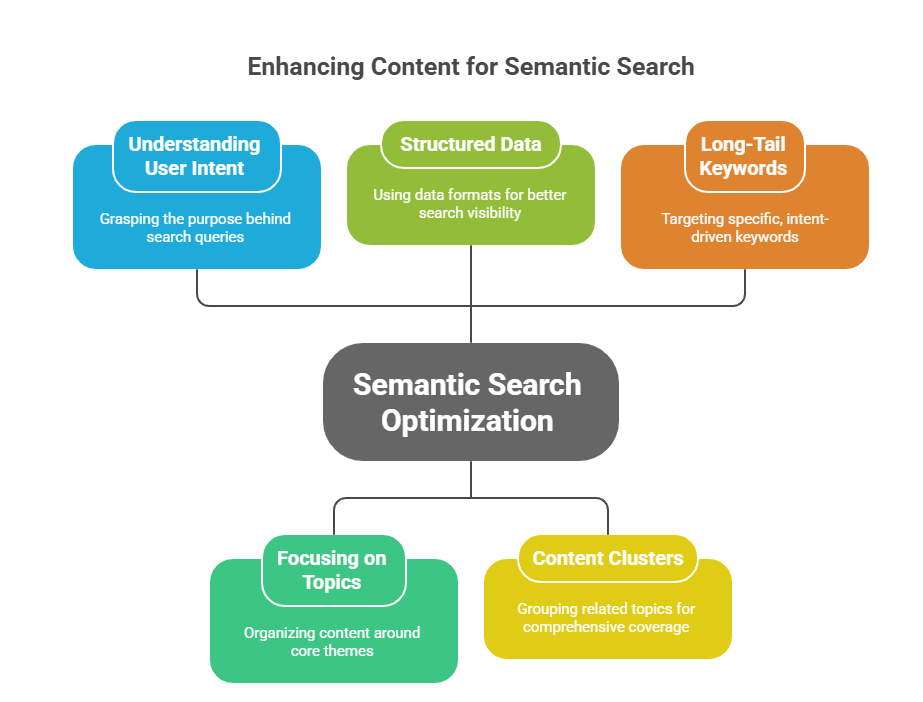
How to Optimize Content for Semantic Search
Optimizing content for semantic search involves more than just inserting keywords. It’s about understanding the intent behind search queries. This requires creating content that addresses potential user questions.
Focusing on topics rather than isolated keywords is crucial. Organize content around core themes that cover subjects in depth. This provides context, helping search engines understand content better.
Optimization Strategies:
- Use structured data for better search visibility
- Create content clusters around related topics
- Leverage long-tail keywords relevant to user intent
Utilizing structured data can enhance content discoverability. It helps search engines accurately interpret and present information. As a result, users receive content that matches their specific needs.
Long-tail keywords can drive more targeted traffic. These phrases reflect natural language usage in queries, aligning well with the principles of semantic search. This alignment boosts content relevance and search performance.
Why Understanding Semantic Search Matters
Understanding semantic search is increasingly vital in today’s digital landscape. It enhances user experience by providing search results that align with the searcher’s intent. This alignment makes searches more intuitive and efficient.
For businesses, leveraging semantic search improves SEO strategies. It ensures content is relevant, thereby increasing visibility and engagement. By mastering semantic search, businesses can stay ahead in the competitive digital environment, optimizing content to meet both user needs and search engine criteria.

 What is Semantic Search? Defining the Concept
What is Semantic Search? Defining the Concept